Although the world looks different in 2020, Rematec and Kemény Boehme & Company (KBC) regard remanufacturing to be an important instrument of after-sales. In the second edition of the exclusive Global Remanufacturing Benchmark (GRB), both organisations have gained insights into remanufacturing trends, developments and challenges. The survey was conducted before and during Rematec Amsterdam (June 2019) and Rematec Asia in Guangzhou, China (October 2019), which allows us to take a closer look at the situation in the European and Asian markets before Covid-19 shook the world. We’ll have a series of articles about industry players and challenges, markets, products and processes, core management, quality and marketing & sales. Today part 3: Products & processes.
Products & processes
The increasing number of environmental policy measures and the great influence of Dieselgate have contributed to the rapid growth of electromobility solutions. This also has a significant impact on remanufacturing of certain products. Remanufacturing is to be expected to take an increasingly important role for certain products, such as electric and hybrid drive units (from 3% today to 16% in the future) as well as electronic components and electronic control units (ECU) (from 8% to 12%) and batteries (from 1% to 8%). With increasing electromobility, combustion-related parts will become less important to the remanufacturing industry. A decrease is expected in combustion engines and parts (from 15% to 10%), starters and alternators (from 18% to 9%) and transmission and transmission parts (from 15% to 12%) (See figure 1). Combustion-related parts will become less and less important with increasing electromobility.
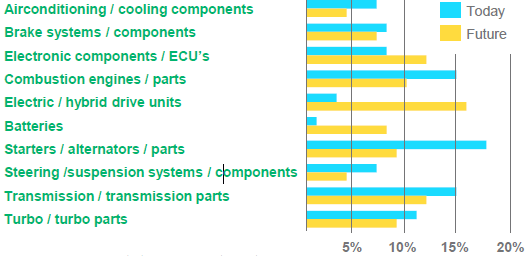
Fig. 1: Focus products today and in the future
Besides, certain core competencies of remanufacturing businesses are to be expected to change. Already today most important competencies are design and development of components and parts (14%), cleaning technology (13%), remanufacturing technology (12%) and recycling, in terms of utilization of residues, which cannot be used for remanufacturing (12%). Other additional competencies will be more and more required in the future. Testing and diagnostics technology, core management, logistics, software and programming and the design and development of remanufacturing equipment and tools will be demanded from future remanufacturing professionals.
Related content
Global remanufacturing benchmark part one: Industry and Challenges
Global remanufacturing benchmark part two: Market
Global remanufacturing benchmark part four: Core management
Global remanufacturing benchmark part five: Quality
Global remanufacturing benchmark part six: Marketing and Sales
More information on the global remanufacturing benchmark






