Although the world looks different in 2020, Rematec and Kemény Boehme & Company (KBC) regard remanufacturing to be an important instrument of after-sales. In the second edition of the exclusive Global Remanufacturing Benchmark (GRB), both organisations have gained insights into remanufacturing trends, developments and challenges. The survey was conducted before and during Rematec Amsterdam (June 2019) and Rematec Asia in Guangzhou, China (October 2019), which allows us to take a closer look at the situation in the European and Asian markets before Covid-19 shook the world. We’ll have a series of articles about industry players and challenges, markets, products and processes, core management, quality and marketing & sales. Today part 4:Core management.
Core management
There are some major challenges of core return:
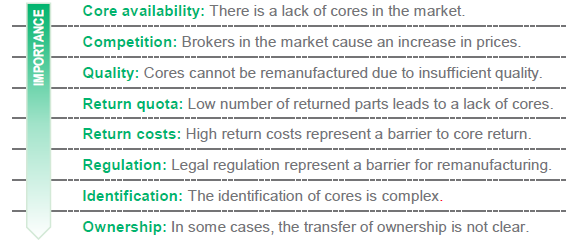
Fig. 1 : Major challenges of core return
There are few main sources of cores for remanufacturing. Most of the remanufacturing professionals surveyed obtain the cores from core dealers (29%). Other important sources are the company’s own products sold without warranty (26%) and warranty return products (26%). Second and third party products also play an important role as a basis for remanufacturing (19%).
To get the cores back from the markets, certain incentives are used for core return. Most of the remanufacturing professionals use deposits and surcharges to incentivise core return (74%) or charge retroactively depending on the core return (26%).
Not every returned part can be used for remanufacturing. The average good core quota of the remanufacturing businesses is 51%, with a range of 0% to 90%. (See figure 2).
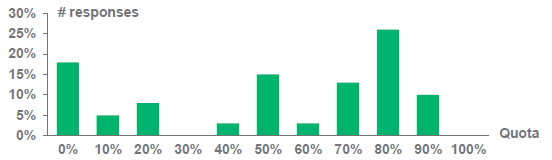
Fig. 2: Good core quota
Related content
Global remanufacturing benchmark part one: Industry and Challenges
Global remanufacturing benchmark part two: Market
Global remanufacturing benchmark part three: Products & Processes
Global remanufacturing benchmark part five: Quality
Global remanufacturing benchmark part six: Marketing and Sales
More information on the global remanufacturing benchmark






